Slug
ambulatory-eeg
Video
Category
Epilepsy
Excerpt
A typical ambulatory electroencephalogram takes place at home while you are conducting your normal daily activities. This is a method of proceeding that employs a portable computer for recording a continuous, prolonged EEG experience over a prolonged period at your residence. In the following sections of this information sheet, you will find information regarding your expectations before, during, and after the examination.
Authors
Tags
Featured
Featured
Ready to Publish
Ready to Publish
Publish Date
Aug 29, 2022

Overview
Electroencephalograms are called EEGs and it is the gold standard in diagnosing a seizure. EEGs record the electrical activity of your brain in a painless manner. In a hospital, an EEG can be performed for a short period of time to record the activity in your brain. An EEG measures how the brain functions at different levels.
There are different types of EEGs. The main difference lies in the location and length of the recording. A regular EEG might not catch an event that occurs less frequently e.g. every 12 to 48 hours. An ambulatory EEG is a longer recording usually between 72 to 96 hours and this longer duration creates an opportunity to catch infrequent events.
Ambulatory EEG
- In an ambulatory EEG, you are monitored from 24 hours to up to 96 hours.
- Ambulatory EEG is recorded at home providing the opportunity to monitor patients in a native environment.
- You will find in this information sheet what to expect before, during, and after the test.
- Any questions you may have about the test should be directed to your doctor. A consent form will need to be signed if you agree to the testing.
- Routine EEGs as are shorter in duration may miss the events in question.
- With continuous longer monitoring like ambulatory EEG, events that are infrequent can be caught.
- Ambulatory is also useful in classifying rarer events like silent seizures, nocturnal or sleep events, syncope (passing out), and pseudo-seizures.
- Ambulatory EEG is now used for memory disturbances as well as to rule out non-convulsive, subclinical seizures as causes of cognitive decline.

Common Indication
🧠 Common Indication:
Event Classification: A patient who experiences this event needs to rule out seizures as a cause of the event:
- R40.4: Transient Alteration of Awareness
- R42: Dizziness & Giddiness
- R55: Syncope & Collapse
Seizure Semiology or Diagnosis: Diagnosis and classification of epilepsy:
- G40.001 - G40.919: Epilepsy and Recurrent Seizures
- R56.9: Post Traumatic Seizures
- R56.1: Unspecified convulsions
Moreover, your treating physician may suggest you perform an ambulatory EEG in case your doctor decides that you have a case of any other uncommon cause not listed above.
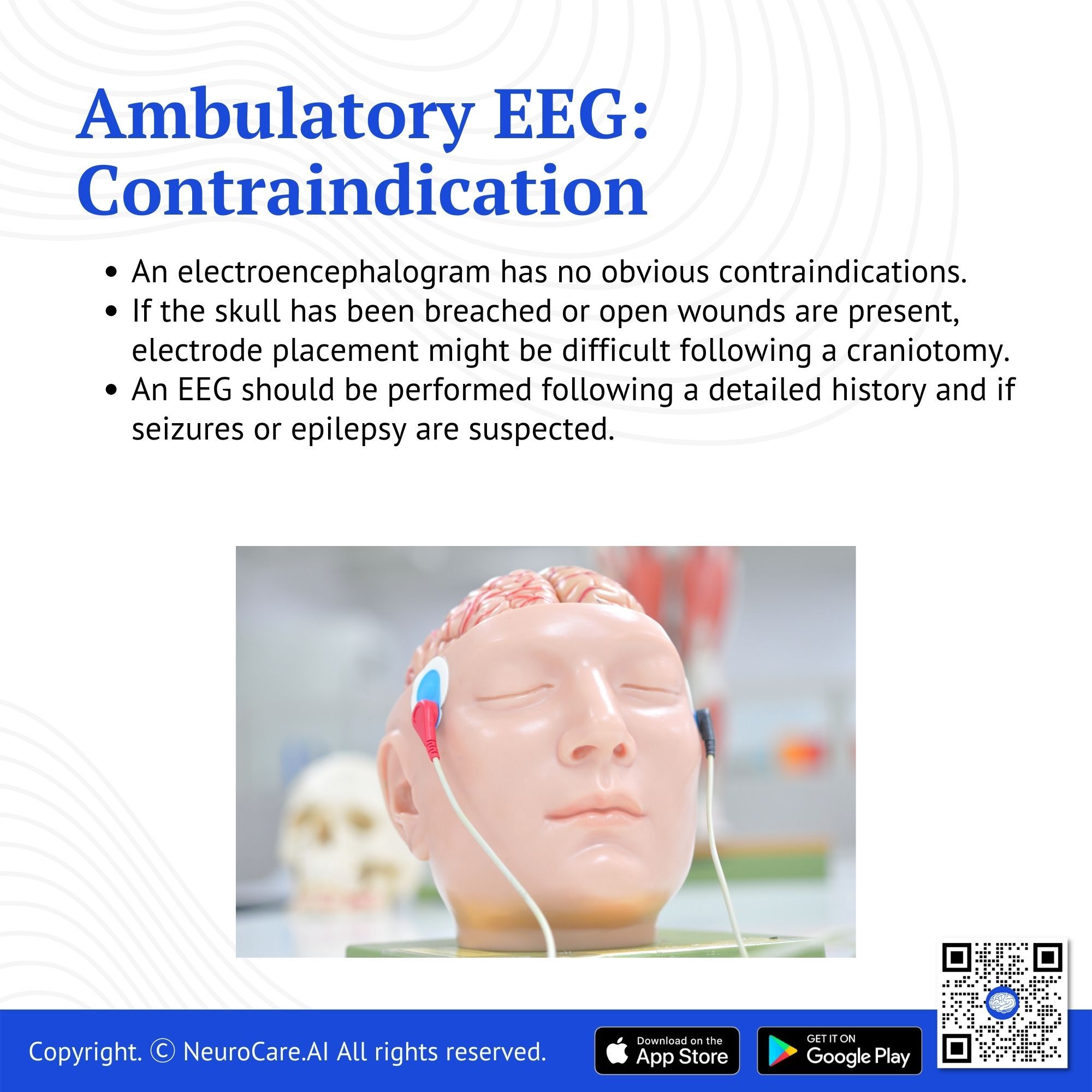
Contraindication
An electroencephalogram has no obvious contraindications. If the skull has been breached or open wounds are present, electrode placement might be difficult following a craniotomy. An EEG should be performed following a detailed history and if seizures or epilepsy are suspected.
What can you expect in an ambulatory EEG?

Pre-Testing Preparations
Make sure you wash your hair with only shampoo and water the night before your appointment. A hair product such as conditioner, oil, gel, or hairspray should not be used. Remove braids, wigs, and hair extensions before the test, as they cannot be worn. Remove any liquid or powder foundation makeup before the test. Wear comfortable clothing to the test. Make sure your tops open fully in the front and don't go over your head. Attend your appointments with someone and arrange for someone to stay with you at home during the test. Having someone with you can help you record and describe any symptoms or events you are unaware of.
- It is possible to wear a hat, bandana, or scarf made of 100% cotton (optional). This will help conceal the electrodes on your head. An optional loose button-up shirt or jacket is also suitable. You can conceal your equipment this way.

During the Testing
Be sure to keep a diary throughout the test, noting what you do and any symptoms you may have had. Doing so will help your doctor to identify the cause of the activity on the recording. If the electrodes make your head feel itchy, you might scratch it, which might appear as abnormal electroencephalogram activity. For the best results from your study, limit your time staying outside the house to 30 minutes or less.
.
Note: Avoid any of the following:
- Sleeping on plugged-in electric blankets or anything else electrical is not recommended.
- Once the machine (multiple electrodes) is placed on your body, you should refrain from washing, showering, or bathing.
- Sweating during your test will affect your performance adversely. Try to keep cool during the test.
- For this procedure, it is essential to obtain accurate readings. Thus, sit back and relax until you have completed the procedure.
- Refrain to take the EEG machine off during the test.

In the event that you experienced a seizure while on testing,
During a seizure, people subjected to ambulatory EEG often have a button that can turn on a video camera and record the event. Having a witness push the button is advantageous if you are unable to do so. This is helpful for a neurologist to correlate the EEG reading with the occurrence of the event.
.jpg)
Post-Testing Preparations
You can either remove the electrodes at home or have them removed at the office. In order to keep the electrodes in place, the technician will probably use a special glue called collodion to keep them in place. Following the test, the glue is removed with acetone (like nail polish remover).
After the glue has been removed, it is important not to wear anything that touches your head afterward, such as eyeglasses, cellphones, hearing aids, earrings, etc. As the glue dissolves, the items could be damaged.

When will I get the results of the EEG?
A medical team member will review the recording once you have left the department, and then your doctor will receive a report. It may take some time before the results are available. This may take up to three weeks because there is a lot of information to review. At your next visit, your doctor will discuss the results with you when they are ready.
DISCLAIMER:
The information in this document is for general educational purposes only. It is not intended to substitute for personalized medical professional advice. NeuroCare.AI makes every effort to provide accurate and timely information, but makes no guarantee in this regard and disclaims responsibility for adverse consequences resulting from its use. For further information, consult a physician and the organization referred to herein.
AizaMD™: Revolutionizing Clinical Documentation
Discover the power of our ambient clinical documentation system, designed to transform clinical encounters into structured SOAP notes with unmatched ease. Experience exceptional value for less than $3 per day—cheaper than your daily coffee!
- Save Time: Free up over 90 minutes daily for each provider.
- Boost Revenue: Increase daily revenue by at least $1,000 per provider.
- Enhance Coding Quality: Our detailed documentation supports superior coding accuracy, ensuring optimal reimbursement.
- Maximize Engagement and Interaction: Dedicate more time to patient care and less to typing, fostering richer and more effective conversations between clinicians and patients
AizaMD™: Automated Radiology Report Generation!
Discover our breakthrough Radiology AI reporting platform built on Ambient AI. It enhances productivity and minimizes fatigue. Benefit from best-in-class accuracy with our automated radiology report generation, all at market-leading pricing.
📈 Efficiency: Cut dictation times by up to 50% (Less words, More report!
🎯 Focus: Keep your eyes on the images, not the keyboard!
💸 Revenue: Boost revenue by at least 20%
📑 Clarity: Patient summary in plain English



